Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Hypothalamus and pituitary gland
- Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone-Secreting Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumor (TSH PitNET): A Single-Center Experience
- Jung Heo, Yeon-Lim Suh, Se Hoon Kim, Doo-Sik Kong, Do-Hyun Nam, Won-Jae Lee, Sung Tae Kim, Sang Duk Hong, Sujin Ryu, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):387-396. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1877
- 843 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
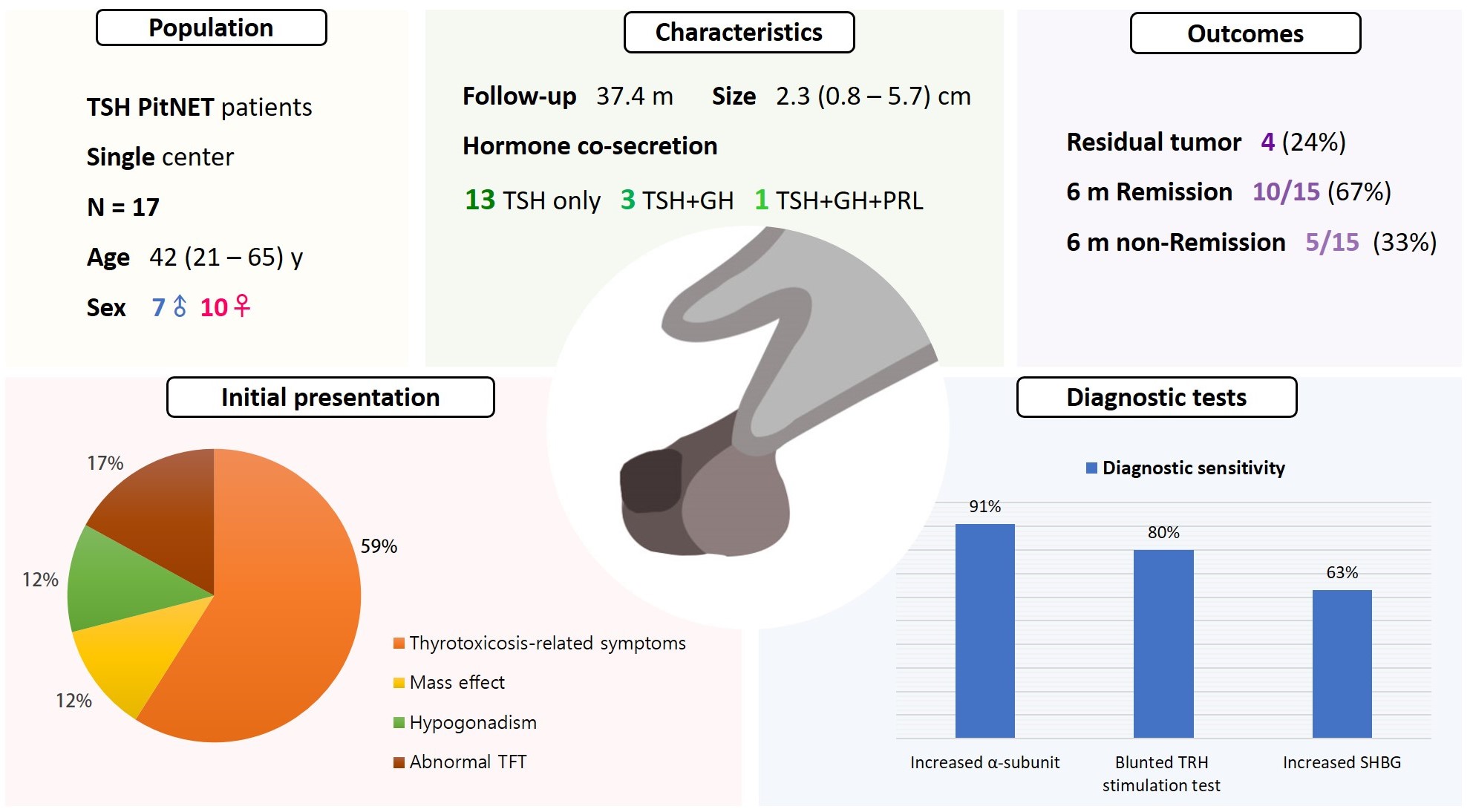
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-secreting pituitary neuroendocrine tumor (TSH PitNET) is a rare subtype of PitNET. We investigated the comprehensive characteristics and outcomes of TSH PitNET cases from a single medical center. Also, we compared diagnostic methods to determine which showed superior sensitivity.
Methods
A total of 17 patients diagnosed with TSH PitNET after surgery between 2002 and 2022 in Samsung Medical Center was retrospectively reviewed. Data on comprehensive characteristics and treatment outcomes were collected. The sensitivities of diagnostic methods were compared.
Results
Seven were male (41%), and the median age at diagnosis was 42 years (range, 21 to 65); the median follow-up duration was 37.4 months. The most common (59%) initial presentation was hyperthyroidism-related symptoms. Hormonal co-secretion was present in four (23%) patients. Elevated serum alpha-subunit (α-SU) showed the greatest diagnostic sensitivity (91%), followed by blunted response at thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) stimulation (80%) and elevated sex hormone binding globulin (63%). Fourteen (82%) patients had macroadenoma, and a specimen of one patient with heavy calcification was negative for TSH. Among 15 patients who were followed up for more than 6 months, 10 (67%) achieved hormonal and structural remission within 6 months postoperatively. A case of growth hormone (GH)/TSH/prolactin (PRL) co-secreting mixed gangliocytoma-pituitary adenoma (MGPA) was discovered.
Conclusion
The majority of the TSH PitNET cases was macroadenoma, and 23% showed hormone co-secretion. A rare case of GH/TSH/PRL co-secreting MGPA was discovered. Serum α-SU and TRH stimulation tests showed great diagnostic sensitivity. Careful consideration is needed in diagnosing TSH PitNET. Achieving remission requires complete tumor resection. In case of nonremission, radiotherapy or medical therapy can improve the long-term remission rate.

- Adrenal Gland
- Urinary Free Metanephrines for Diagnosis of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma
- Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Yun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Soo-Youn Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):697-701. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.925
- 4,390 View
- 188 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
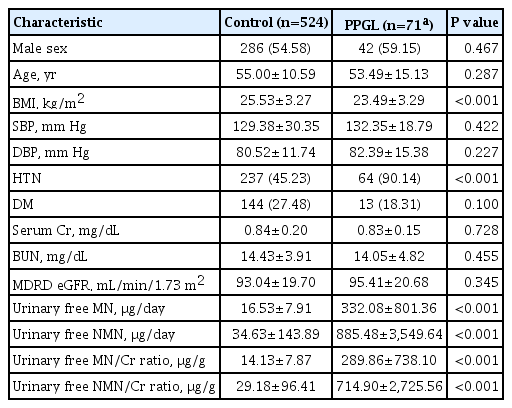
Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL) is diagnosed through biochemical confirmation of excessive catecholamines in urine and plasma. Recent technological developments have allowed us to measure urinary free metanephrines; however, the diagnostic accuracy of these new methods and the diagnostic cutoff values have not been evaluated.
Methods
This is a retrospective study of 595 subjects, including 71 PPGL cases and 524 controls. PPGL was based on pathological confirmation. Subjects with no evidence of PPGL over 2 years were included in the control group.
Results
Urinary free metanephrines yielded similar area under the curve (AUC) to urinary fractionated metanephrines and plasma free metanephrines. However, urinary free normetanephrine yielded a better AUC than did urinary fractionated normetanephrine. The optimal cutoff for urinary free metanephrine and normetanephrine corrected for urinary creatinine yielded 97.2% sensitivity and 98.1% specificity.
Conclusion
Urinary free metanephrines are a reliable method for diagnosing PPGL in Asian populations compared with existing biochemical methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical Assessment of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma
Graeme Eisenhofer, Christina Pamporaki, Jacques W M Lenders
Endocrine Reviews.2023; 44(5): 862. CrossRef - Adrenal bleeding due to pheochromocytoma - A call for algorithm
Ewelina Rzepka, Joanna Kokoszka, Anna Grochowska, Magdalena Ulatowska-Białas, Martyna Lech, Marta Opalińska, Elwira Przybylik-Mazurek, Aleksandra Gilis-Januszewska, Alicja Hubalewska-Dydejczyk
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Biochemical Assessment of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma

- Clinical Study
- Association of Body Mass Index with the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and All-Cause Mortality: A Community-Based Prospective Study
- Ji Cheol Bae, Nam H. Cho, Jae Hyeon Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sang-Man Jin, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):416-424. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.416

- 8,115 View
- 156 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD) are the most important sequelae of obesity and the leading cause of death. We evaluated the association between body mass index (BMI) and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes, CVD, and all-cause mortality in a prospective study of a Korean population.
Methods
The shapes of the associations were modeled by restricted cubic splines regression analysis. After categorizing all subjects (n=8,900) into octiles based on their BMI levels, we estimated the hazard ratio (HR) for the association of categorized BMI levels with the risk of incident CVD and type 2 diabetes using a Cox’s proportional hazard analysis.
Results
The mean age of participants was 52 years and 48% were men. Of the subjects at baseline, 39.0% of men and 45.6% of women were classified as obese (BMI ≥25 kg/m2). Over a mean follow-up of 8.1 years, CVD events occurred in 509 participants; 436 died; and 1,258 subjects developed type 2 diabetes. The increased risk of incident diabetes began to be significant at BMI 23 to 24 kg/m2 in both sexes (HR, 1.8). For CVD events, the risk began to increase significantly at BMI 26 to 28 kg/m2 (HR, 1.6). We found a reverse J-shaped relationship between BMI and all-cause mortality, with an increased risk among individuals with BMI values in lower range (BMI <21 kg/m2).
Conclusion
These results suggest that the BMI cut-off points for observed risk were varied depending on the diseases and that the BMI classification of obesity need to be revised to reflect differential risk of obesity-related diseases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of obesity with cardiovascular disease in the absence of traditional risk factors
Hui Luo, Yesong Liu, Xue Tian, Yuhan Zhao, Lulu Liu, Zemeng Zhao, Lili Luo, Yanmin Zhang, Xiaozhong Jiang, Yeqiang Liu, Yanxia Luo, Anxin Wang
International Journal of Obesity.2024; 48(2): 263. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and degree of cardiovascular risk factor control in patients with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes in Catalonia
Anna Ramírez-Morros, Josep Franch-Nadal, Jordi Real, Queralt Miró-Catalina, Magdalena Bundó, Bogdan Vlacho, Didac Mauricio
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic status indicators and influencing factors in non-obese, non-centrally obese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Zhipeng Huang, Donghong Wei, Xueping Yu, Zicheng Huang, Yijie Lin, Wenji Lin, Zhijun Su, Jianjia Jiang
Medicine.2023; 102(6): e32922. CrossRef - Establishment and health management application of a prediction model for high-risk complication combination of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on data mining
Xin Luo, Jijia Sun, Hong Pan, Dian Zhou, Ping Huang, Jingjing Tang, Rong Shi, Hong Ye, Ying Zhao, An Zhang, Yee Gary Ang
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(8): e0289749. CrossRef - Differential Impact of Obesity on the Risk of Diabetes Development in Two Age Groups: Analysis from the National Health Screening Program
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Yang-Hyun Kim, Ga Eun Nam, Sang Hyun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 846. CrossRef - Relationship between advanced lung cancer inflammation index and long-term all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: NHANES, 1999–2018
Yaying Chen, Mengqian Guan, Ruiqi Wang, Xuewen Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Body mass index at baseline directly predicts new-onset diabetes and to a lesser extent incident cardio-cerebrovascular events, but has a J-shaped relationship to all-cause mortality
Yoon-Jong Bae, Sang-Jun Shin, Hee-Taik Kang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Shift Work with Normal-Weight Obesity in Community-Dwelling Adults
Chul Woo Ahn, Sungjae Shin, Seunghyun Lee, Hye-Sun Park, Namki Hong, Yumie Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 781. CrossRef - The Prognostic Value of Combined Status of Body Mass Index and Psychological Well-Being for the Estimation of All-Cause and CVD Mortality Risk: Results from a Long-Term Cohort Study in Lithuania
Dalia Lukšienė, Abdonas Tamosiunas, Ricardas Radisauskas, Martin Bobak
Medicina.2022; 58(11): 1591. CrossRef - The Relationship between Body Mass Index and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Aged Population: A Cohort Study
M. L. Tang, Y. Q. Zhou, A. Q. Song, J. L. Wang, Y. P. Wan, R. Y. Xu, Carol Forsblom
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Correlation between adiponectin level and the degree of fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Manal Sabry Mohamed, Tarek Mohammed Youssef, Esraa Ebrahim Abdullah, Ahmed Elmetwally Ahmed
Egyptian Liver Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity Measures as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases among the Jordanian Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
Hana Alkhalidy, Aliaa Orabi, Khadeejah Alnaser, Islam Al-Shami, Tamara Alzboun, Mohammad D. Obeidat, Dongmin Liu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(22): 12187. CrossRef
- Association of obesity with cardiovascular disease in the absence of traditional risk factors

- Clinical Study
- Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Peptide Level Is Associated with the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Sunghwan Suh, Mi Yeon Kim, Soo Kyoung Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Mi Kyoung Park, Duk Kyu Kim, Nam H. Cho, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):134-141. Published online March 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.134
- 3,814 View
- 44 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Incretin hormone levels as a predictor of type 2 diabetes mellitus have not been fully investigated. Therefore, we measured incretin hormone levels to examine the relationship between circulating incretin hormones, diabetes, and future diabetes development in this study.
Methods A nested case-control study was conducted in a Korean cohort. The study included the following two groups: the control group (
n =149), the incident diabetes group (n =65). Fasting total glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and total glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) levels were measured and compared between these groups.Results Fasting total GIP levels were higher in the incident diabetes group than in the control group (32.64±22.68 pmol/L vs. 25.54±18.37 pmol/L,
P =0.034). There was no statistically significant difference in fasting total GLP-1 levels between groups (1.14±1.43 pmol/L vs. 1.39±2.13 pmol/L,P =0.199). In multivariate analysis, fasting total GIP levels were associated with an increased risk of diabetes (odds ratio, 1.005;P =0.012) independent of other risk factors.Conclusion Fasting total GIP levels may be a risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. This association persisted even after adjusting for other metabolic parameters such as elevated fasting glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and obesity in the pre-diabetic period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mendelian randomization analyses suggest a causal role for circulating GIP and IL-1RA levels in homeostatic model assessment-derived measures of β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in Africans without type 2 diabetes
Karlijn A. C. Meeks, Amy R. Bentley, Themistocles L. Assimes, Nora Franceschini, Adebowale A. Adeyemo, Charles N. Rotimi, Ayo P. Doumatey
Genome Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose- and Bile Acid-Stimulated Secretion of Gut Hormones in the Isolated Perfused Intestine Is Not Impaired in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Jenna E. Hunt, Jens J. Holst, Sara L. Jepsen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined treatment with a gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor antagonist and a peptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor improves metabolic abnormalities in diabetic mice
Fei Yang, Shan Dang, Hongjun LV, Bingyin Shi
Journal of International Medical Research.2021; 49(1): 030006052098566. CrossRef - Elevated levels of fasting serum GIP may be protective factors for diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus
LingHong Huang, JingXiong Zhou, Bo Liang, HuiBin Huang, LiangYi Li
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(4): 543. CrossRef - Enteroendocrine K and L cells in healthy and type 2 diabetic individuals
Tina Jorsal, Nicolai A. Rhee, Jens Pedersen, Camilla D. Wahlgren, Brynjulf Mortensen, Sara L. Jepsen, Jacob Jelsing, Louise S. Dalbøge, Peter Vilmann, Hazem Hassan, Jakob W. Hendel, Steen S. Poulsen, Jens J. Holst, Tina Vilsbøll, Filip K. Knop
Diabetologia.2018; 61(2): 284. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef
- Mendelian randomization analyses suggest a causal role for circulating GIP and IL-1RA levels in homeostatic model assessment-derived measures of β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in Africans without type 2 diabetes

- Adrenal gland
- Clinical Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cushing's Disease in Korea
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Jung Hee Kim, Byung Joon Kim, Min-Seon Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Sung-Woon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):7-18. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.7
- 6,696 View
- 151 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Cushing's disease (CD) is a rare disorder characterized by the overproduction of adrenocorticotropic hormone due to a pituitary adenoma that ultimately stimulates excessive cortisol secretion from the adrenal glands. Prior to the detection of pituitary adenomas, various clinical signs of CD such as central obesity, moon face, hirsutism, and facial plethora are usually already present. Uncontrolled hypercortisolism is associated with metabolic, cardiovascular, and psychological disorders that result in increased mortality. Hence, the early detection and treatment of CD are not only important but mandatory. Because its clinical manifestations vary from patient to patient and are common in other obesity-related conditions, the precise diagnosis of CD can be problematic. Thus, the present set of guidelines was compiled by Korean experts in this field to assist clinicians with the screening, diagnoses, and treatment of patients with CD using currently available tests and treatment modalities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diet quality and dietary acid load in relation to cardiovascular disease mortality: Results from Fasa PERSIAN cohort study
Sahar Fereidouni, Najmeh Hejazi, Reza Homayounfar, Mojtaba Farjam
Food Science & Nutrition.2023; 11(3): 1563. CrossRef - Role of computed tomography in predicting adrenal adenomas with cortisol hypersecretion
Chan Kyo Kim, Kyung A Kang, Young Lyun Oh, Sung Yoon Park
The British Journal of Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary acid load and mortality from all causes, CVD and cancer: results from the Golestan Cohort Study
Ehsan Hejazi, Hadi Emamat, Maryam Sharafkhah, Atoosa Saidpour, Hossein Poustchi, Sadaf Sepanlou, Masoud Sotoudeh, Sanford Dawsey, Paolo Boffetta, Christian C Abnet, Farin Kamangar, Arash Etemadi, Akram Pourshams, Akbar Fazeltabar Malekshah, Paul Berennan,
British Journal of Nutrition.2022; 128(2): 237. CrossRef - Forty Years Together, New Leap Forward! The 40th Anniversary of the Korean Endocrine Society
Jong Chul Won, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 851. CrossRef - Pituitary adenomas: current principles of diagnosis and treatment
L. I. Astafyeva, I. V. Chernov, I. V. Chekhonin, E. I. Shults, I. N. Pronin, P. L. Kalinin
Russian journal of neurosurgery.2021; 22(4): 94. CrossRef - Metabolic changes in serum steroids for diagnosing and subtyping Cushing’s syndrome
Chang Ho Ahn, Chaelin Lee, Jaeyoon Shim, Sung Hye Kong, Su-jin Kim, Yong Hwy Kim, Kyu Eun Lee, Chan Soo Shin, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2021; 210: 105856. CrossRef - Application of different variants of endoscopic transphenoidal removal of corticotropinomas in order to increase the frequency and duration of remission
A. Ashraf, I. V. Chernov, A. N. Shkarubo, M. A. Kutin, D. V. Fomichev, O. I. Sharipov, Yu. Yu. Trunin, D. N. Andreev, A. A. Abdilatipov, L. I. Astafieva, B. Abdali, A. B. Kurnosov, G. E. Chmutin, Kalinin P. L. Kalinin P. L.
Vestnik nevrologii, psihiatrii i nejrohirurgii (Bulletin of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery).2021; (2): 143. CrossRef - Modern aspects of surgery for cushing’s disease
A. Abdali, L.I. Astafeva, Yu.Yu. Trunin, I.V. Chernov, Yu.G. Sidneva, A.A. Abdilatipov, P.L. Kalinin
Voprosy neirokhirurgii imeni N.N. Burdenko.2021; 85(4): 111. CrossRef - Pituitary microadenomas — current diagnostic and treatment methods
L.I. Astafyeva, B.A. Kadashev, Yu.G. Sidneva, I.V. Chernov, P.L. Kalinin
Voprosy neirokhirurgii imeni N.N. Burdenko.2020; 84(2): 110. CrossRef - Usefulness of prolactin measurement in inferior petrosal sinus sampling with desmopressin for Cushing’s syndrome
Hamideh Akbari, Mohammad Ghorbani, Maryam Kabootari, Ali Zare Mehrjardi, Mohammad Reza Mohajeri Tehrani, Mojtaba Malek, Mohammad E. Khamseh
British Journal of Neurosurgery.2020; 34(3): 253. CrossRef - Hormonal aggressiveness according to the expression of cellular markers in corticotroph adenomas
Jung Soo Lim, Mi-Kyung Lee, Eunhee Choi, Namki Hong, Soo Il Jee, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrine.2019; 64(1): 147. CrossRef - Clinical Parameters to Distinguish Silent Corticotroph Adenomas from Other Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas
Daham Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Se Hee Park, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
World Neurosurgery.2018; 115: e464. CrossRef - Blood Tests for the Diagnosis of Adrenal Diseases
Seon-Ah Cha, Sung-Dae Moon
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2018; 93(6): 532. CrossRef - Choosing wisely: la lista del gruppo di studio Endocrinologia e Malattie del Metabolismo della Società Italiana di Patologia Clinica e Medicina di Laboratorio
Romolo M. Dorizzi, Anna Ferrari, Marina Vitillo, Beatrice Caruso, Claudio Cocco, Erennio Ciotoli, Federica D’Aurizio, Elisa Esposito, Germana Giannone, Giulio Ozzola, Ottavia Porzio, Emanuela Toffalori, Renato Tozzoli
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio - Italian Journal of Laboratory Medicine.2016; 12(2): 81. CrossRef - Surgical management of adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas
Edwin S Kulubya, Daniel A Donoho, John D Carmichael, Gabriel Zada
International Journal of Endocrine Oncology.2016; 3(1): 41. CrossRef
- Diet quality and dietary acid load in relation to cardiovascular disease mortality: Results from Fasa PERSIAN cohort study

- Adrenal gland
- Clinical Characteristics, Management, and Outcome of 22 Cases of Primary Hypophysitis
- Sun Mi Park, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Young Joung, Yoon Young Cho, Tae Hun Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sunghwan Suh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kwang-Won Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):470-478. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.470
- 4,240 View
- 41 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Primary hypophysitis causes varying degrees of endocrine dysfunction and mass effect. The natural course and best treatment have not been well established.
Methods Medical records of 22 patients who had been diagnosed with primary hypophysitis between January 2001 and March 2013 were retrospectively reviewed. Based on the anatomical location, we classified the cases as adenohypophysitis (AH), infundibuloneurohypophysitis (INH), and panhypophysitis (PH). Clinical presentation, endocrine function, pathologic findings, magnetic resonance imaging findings, and treatment courses were reviewed.
Results Among 22 patients with primary hypophysitis, 81.8% (18/22) had involvement of the posterior pituitary lobe. Two patients of the AH (2/3, 66.6%) and three patients of the PH (3/10, 30%) groups initially underwent surgical mass reduction. Five patients, including three of the PH (3/10, 33.3%) group and one from each of the AH (1/3, 33.3%) and INH (1/9, 11.1%) groups, initially received high-dose glucocorticoid treatment. Nearly all of the patients treated with surgery or high-dose steroid treatment (9/11, 82%) required continuous hormone replacement during the follow-up period. Twelve patients received no treatment for mass reduction due to the absence of acute symptoms and signs related to a compressive mass effect. Most of them (11/12, 92%) did not show disease progression, and three patients recovered partially from hormone deficiency.
Conclusion Deficits of the posterior pituitary were the most common features in our cases of primary hypophysitis. Pituitary endocrine defects responded less favorably to glucocorticoid treatment and surgery. In the absence of symptoms related to mass effect and with the mild defect of endocrine function, it may not require treatment to reduce mass except hormone replacement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Secondary xanthogranulomatous hypophysitis mimicking a pituitary macroadenoma: a case report
Salma Salhi, Ibtissem Oueslati, Yasmine Mouelhi, Alia Zehani, Nidhameddine Kchir, Elyes Kamoun, Meriem Yazidi, Melika Chihaoui
Journal of International Medical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucocorticoid therapy as first-line treatment in primary hypophysitis: a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis
Brijesh Krishnappa, Ravikumar Shah, Saba Samad Memon, Chakra Diwaker, Anurag R Lila, Virendra A Patil, Nalini S Shah, Tushar R Bandgar
Endocrine Connections.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypophysitis, the Growing Spectrum of a Rare Pituitary Disease
Fabienne Langlois, Elena V Varlamov, Maria Fleseriu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(1): 10. CrossRef - Outcomes of Initial Management Strategies in Patients With Autoimmune Lymphocytic Hypophysitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Diane Donegan, Zeb Saeed, Danae A Delivanis, Mohammad Hassan Murad, Juergen Honegger, Felix Amereller, Seda Hanife Oguz, Dana Erickson, Irina Bancos
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(4): 1170. CrossRef - Early Pulse Glucocorticoid Therapy and Improved Hormonal Outcomes in Primary Hypophysitis
Brijesh Krishnappa, Ravikumar Shah, Vijaya Sarathi, Anurag Ranjan Lila, Manjeet Kaur Sehemby, Virendra A. Patil, Shilpa Sankhe, Nalini Shah, Tushar Bandgar
Neuroendocrinology.2022; 112(2): 186. CrossRef - Preoperative differentiation of hypophysitis and pituitary adenomas using a novel clinicoradiologic scoring system
Kyla Wright, Hyon Kim, Travis Hill, Matthew Lee, Cordelia Orillac, Nikita Mogar, Donato Pacione, Nidhi Agrawal
Pituitary.2022; 25(4): 602. CrossRef - Hypophysitis
Diane Donegan, Jürgen Honegger
Endocrine Practice.2022; 28(9): 901. CrossRef - Rare Case of a Disappearing Pituitary Adenoma During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic
David P. Bray, C. Arturo Solares, Nelson M. Oyesiku
World Neurosurgery.2021; 146: 148. CrossRef - Diabetes insipidus secondary to sellar/parasellar lesions
Anna Angelousi, Chrysoula Mytareli, Paraskevi Xekouki, Eva Kassi, Konstantinos Barkas, Ashley Grossman, Gregory Kaltsas
Journal of Neuroendocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical presentation and management of hypophysitis: An observational study of case series
Marouan Karrou, Salma Benyakhlef, Achwak Alla, Najoua Messaoudi, Asmae Oulad Amar, Siham Rouf, Imane Kamaoui, Noureddine Oulali, Faycal Moufid, Naima Abda, Hanane Latrech
Surgical Neurology International.2021; 12: 304. CrossRef - Clinical aspects of autoimmune hypothalamitis, a variant of autoimmune hypophysitis: Experience from one center
Qian Wei, Guoqing Yang, Zhaohui Lue, Jingtao Dou, Li Zang, Yijun Li, Jin Du, Weijun Gu, Yiming Mu
Journal of International Medical Research.2020; 48(3): 030006051988783. CrossRef - Primary and Ipilimumab-induced Hypophysitis: A Single-center Case Series
Paul Atkins, Ehud Ur
Endocrine Research.2020; 45(4): 246. CrossRef - Hypophysitis (Including IgG4 and Immunotherapy)
Anna Angelousi, Krystallenia Alexandraki, Marina Tsoli, Gregory Kaltsas, Eva Kassi
Neuroendocrinology.2020; 110(9-10): 822. CrossRef - Hypophysitis in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors and immunoglobulin G4-related disease
Leen Wehbeh, Sama Alreddawi, Roberto Salvatori
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 14(3): 167. CrossRef - Immune check point inhibitors-induced hypophysitis: a retrospective analysis of the French Pharmacovigilance database
Julie Garon-Czmil, Nadine Petitpain, Franck Rouby, Marion Sassier, Samy Babai, Mélissa Yéléhé-Okouma, Georges Weryha, Marc Klein, Pierre Gillet
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Features, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Treatment Experience of 20 Patients with Lymphocytic Hypophysitis in a Single Center
Qiang Zhu, Ke Qian, Guijun Jia, Gang Lv, Jisheng Wang, Liyong Zhong, Shuqing Yu
World Neurosurgery.2019; 127: e22. CrossRef - Idiopathic granulomatous hypophysitis presenting with galactorrhea, headache, and nausea in a woman: a case report and review of the literature
Guive Sharifi, Mohammad Reza Mohajeri-Tehrani, Behrouz Navabakhsh, Bagher Larijani, Touraj Valeh
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Paciente de 31 años con polidipsia
A.R. Benavides Aramburu, M. Seguí Díaz
Medicina de Familia. SEMERGEN.2018; 44(2): e77. CrossRef - Primary hypophysitis and other autoimmune disorders of the sellar and suprasellar regions
Sriram Gubbi, Fady Hannah-Shmouni, Constantine A. Stratakis, Christian A. Koch
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2018; 19(4): 335. CrossRef - Primary lymphocytic hypophysitis: Clinical characteristics and treatment of 50 cases in a single centre in China over 18 years
Shuchang Wang, Linjie Wang, Yong Yao, Feng Feng, Hongbo Yang, Zhiyong Liang, Kan Deng, Hui You, Jian Sun, Bing Xing, Zimeng Jin, Renzhi Wang, Hui Pan, Huijuan Zhu
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 87(2): 177. CrossRef - Clinical presentation and outcome of children with central diabetes insipidus associated with a self‐limited or transient pituitary stalk thickening, diagnosed as infundibuloneurohypophysitis
J. Schaefers, M. Cools, K. De Waele, I. Gies, V. Beauloye, P. Lysy, I. Francois, D. Beckers, J. De Schepper
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 87(2): 171. CrossRef - Intrachiasmatic abscess caused by IgG4-related hypophysitis
Georgios F. Hadjigeorgiou, Eva Løbner Lund, Lars Poulsgaard, Ulla Feldt-Rasmussen, Åse Krogh Rasmussen, Marianne Wegener, Kåre Fugleholm
Acta Neurochirurgica.2017; 159(11): 2229. CrossRef - Granulomatous and lymphocytic hypophysitis – are they immunologically distinct?
Shilpa Rao, Anita Mahadevan, Tanmoy Maiti, Manish Ranjan, Shivayogi Durgad Shwetha, Arimappamagan Arivazhagan, Jitender Saini
APMIS.2016; 124(12): 1072. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Secondary xanthogranulomatous hypophysitis mimicking a pituitary macroadenoma: a case report

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Association between Serum Albumin, Insulin Resistance, and Incident Diabetes in Nondiabetic Subjects
- Ji Cheol Bae, Sung Hwan Seo, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Myung-Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Won Young Lee, Eun Jung Rhee, Ki Won Oh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(1):26-32. Published online March 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.1.26
- 4,588 View
- 42 Download
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Serum albumin has been suggested to be associated with insulin resistance. We evaluated the association between serum albumin concentration and insulin resistance. We also investigated whether serum albumin level has an independent effect on the development of diabetes.
Methods In our study, 9,029 subjects without diabetes, who underwent comprehensive health check-ups annually for 5 years, were categorized into tertiles based on their serum albumin levels at baseline. The odds ratio (OR) for the prevalence of insulin resistance, defined as the top quartile of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance and the presence of impaired fasting glucose and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, was evaluated cross-sectionally. Also, the hazard ratio (HR) for incident diabetes was estimated longitudinally, according to the baseline albumin tertiles using Cox proportional hazard analysis respectively.
Results From the lowest to the highest tertile of albumin, the multivariable-adjusted ORs of insulin resistance increased significantly in both men and women. During the mean follow-up period of nearly 4 years, 556 (6.1%) subjects progressed to diabetes. The multivariable-adjusted HR (95% confidence interval [CI]) of diabetes in men were 1, 1.09 (95% CI, 0.86 to 1.40), and 1.10 (95% CI, 0.86 to 1.41), respectively, from the lowest to the highest tertiles of baseline albumin. Corresponding values for women were 1, 1.21 (95% CI, 0.66 to 2.21), and 1.06 (95% CI, 0.56 to 2.02), respectively.
Conclusion Our study showed that increased serum albumin level was associated with insulin resistance. However, serum albumin did not have an independent effect on the development of diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Detected by Computed Tomography in the General Population Compared with Ultrasonography
Yuki Ito, Kentaro Yoshioka, Kazuhiko Hayashi, Yuko Shimizu, Ryo Fujimoto, Ryosuke Yamane, Michiyo Yoshizaki, Go Kajikawa, Taro Mizutani, Hidemi Goto
Internal Medicine.2024; 63(2): 159. CrossRef - Geriatric nutritional risk index is correlated with islet function but not insulin resistance in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective study
Nan Geng, Yaxue Gao, Yuanyuan Ji, Yingchun Niu, Cuijuan Qi, Yunfeng Zhen, Jinhu Chen, Luping Ren
Medicine.2024; 103(11): e37438. CrossRef - Blood Urea Nitrogen to Serum Albumin Ratio as A New Prognostic
Indicator in Critically Ill Patients with Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Retrospective
Cohort Study
Tingting Hang, Jing Huang, Guiping He, Jin Li, Tingting Tao
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex difference in the associations among liver function parameters with incident diabetes mellitus in a large Taiwanese population follow-up study
Yi-Kong Chen, Pei-Yu Wu, Jiun-Chi Huang, Szu-Chia Chen, Jer-Ming Chang
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antidiabetic Properties of Nymphaea Species (Water Lilies): A Review
A. H. M. Safayet Ullah Prodhan, Farzana Sharmin Mridu
The Natural Products Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational diabetes in women living with HIV in the UK and Ireland: insights from population‐based surveillance data
Laurette L. Bukasa, Mario Cortina‐Borja, Helen Peters, Graham P. Taylor, Claire Thorne
Journal of the International AIDS Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer and Diabetes: Predictive Factors in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Mihai Cosmin Stan, Daniel Georgescu, Ciprian Camil Mireștean, Florinel Bădulescu
Diagnostics.2023; 13(16): 2647. CrossRef - Role of liver parameters in diabetes mellitus – a narrative review
Sana Rafaqat, Aqsa Sattar, Amber Khalid, Saira Rafaqat
Endocrine Regulations.2023; 57(1): 200. CrossRef - Differential cellular responses to FDA-approved nanomedicines: an exploration of albumin-based nanocarriers and liposomes in protein corona formation
Athika Darumas Putri, Ming-Jen Hsu, Chia-Li Han, Fang-Ching Chao, Chun-Hua Hsu, Christian D. Lorenz, Chien-Ming Hsieh
Nanoscale.2023; 15(44): 17825. CrossRef - Association of the HALP Score with Dyslipidemia: A Large, Nationwide Retrospective Study
Yazeed Alshuweishi, Ahmed M. Basudan, Mohammed Alfaifi, Hussam Daghistani, Mohammad A. Alfhili
Medicina.2023; 59(11): 2002. CrossRef - Preventive and Ameliorative Effects of Diet Supplemented with Cucurbita maxima Leaf on Hyperglycemia and Hepatotoxicity in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats
Job Itanyi Onuche, Arowora Kayode Adebisi , Joseph Ikwebe, Michael Sunday Abu
Asian Journal of Biological Sciences.2023; 16(4): 502. CrossRef - Lower Plasma Albumin, Higher White Blood Cell Count and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein are Associated with Femoral Artery Intima-Media Thickness Among Newly Diagnosed Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Nga Phi Thi Nguyen, Thuc Luong Cong, Thi Thanh Hoa Tran, Binh Nhu Do, Son Tien Nguyen, Binh Thanh Vu, Lan Ho Thi Nguyen, Manh Van Ngo, Hoa Trung Dinh, Hoang Duong Huy, Nghia Xuan Vu, Kien Nguyen Trung, Duong Ngoc Vu, Nghia The Pham, Tuan Dinh Le
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 2715. CrossRef - Liver-function parameters are associated with incident hypertension in a large Taiwanese population follow-up study
Yi-Hsueh Liu, Szu-Chia Chen, Wen-Hsien Lee, Ying-Chih Chen, Jiun-Chi Huang, Pei-Yu Wu, Chih-Hsing Hung, Chao-Hung Kuo, Ho-Ming Su
Journal of Human Hypertension.2022; 37(6): 496. CrossRef - Can probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic supplementation modulate the gut-liver axis in type 2 diabetes? A narrative and systematic review of clinical trials
Yousef Al-Najjar, Maryam Arabi, Pradipta Paul, Ali Chaari
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Albumin infusion ameliorates liver injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
CS Bae, T Ahn
Veterinární medicína.2022; 67(5): 245. CrossRef - Ameliorative effect of Annona reticulata L. leaf extract on antihyperglycemic activity and its hepato-renal protective potential in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats
Vineela Pulivarthi, Josthna P., C.V. Naidu
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2021; 12(3): 415. CrossRef - MALDI-TOF MS Characterisation of the Serum Proteomic Profile in Insulin-Resistant Normal-Weight Individuals
Katarzyna Pastusiak, Eliza Matuszewska, Dagmara Pietkiewicz, Jan Matysiak, Pawel Bogdanski
Nutrients.2021; 13(11): 3853. CrossRef - Insulin sensitivity variations in apparently healthy Arab male subjects: correlation with insulin and C peptide
Noor Suleiman, Meis Alkasem, Shaimaa Hassoun, Ibrahem Abdalhakam, Ilham Bettahi, Fayaz Mir, Manjunath Ramanjaneya, Jayakumar Jerobin, Ahmad Iskandarani, Tareq A Samra, Prem Chandra, Monica Skarulis, Abdul Badi Abou-Samra
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2021; 9(2): e002039. CrossRef - U-shaped association between serum albumin and development of chronic kidney disease in general hypertensive patients
Chongfei Jiang, Binyan Wang, Youbao Li, Liling Xie, Xianglin Zhang, Jiancheng Wang, Yaren Yu, Yun Song, Min Liang, Guobao Wang, Jianping Li, Yan Zhang, Lishun Liu, Chengzhang Liu, Genfu Tang, Yong Huo, Xiping Xu, Xianhui Qin
Clinical Nutrition.2020; 39(1): 258. CrossRef - Serum albumin cysteine trioxidation is a potential oxidative stress biomarker of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Selvam Paramasivan, Sunil S. Adav, SoFong Cam Ngan, Rinkoo Dalan, Melvin Khee-Shing Leow, Hee Hwa Ho, Siu Kwan Sze
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum albumin, cardiometabolic and other adverse outcomes: systematic review and meta-analyses of 48 published observational cohort studies involving 1,492,237 participants
Samuel Seidu, Setor K. Kunutsor, Kamlesh Khunti
Scandinavian Cardiovascular Journal.2020; 54(5): 280. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle reprogramming by breast cancer regardless of treatment history or tumor molecular subtype
Hannah E. Wilson, David A. Stanton, Cortney Montgomery, Aniello M. Infante, Matthew Taylor, Hannah Hazard-Jenkins, Elena N. Pugacheva, Emidio E. Pistilli
npj Breast Cancer.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of nutritional deficiencies in bariatric surgery candidates and its effect on metabolic status
Sílvia Cristina de Sousa Paredes, Fernando Mota-Garcia
Hormones.2020; 19(4): 505. CrossRef The Product of Red Blood Cells and Hematocrit Can Be Used as a Novel Indicator of Impaired Fasting Blood Glucose Status
Ling Feng, Haishan Chen, Jianhui Chen, Chongxiang Xiong, Xiaofei Shao, Xin Wang, Jing Ning, Zhicong Xiang, Xuan Wang, Tong Chen, Hua Xiao, Hongjuan Tang, Xiaolin Li, Guobao Hong, Hequn Zou
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4007. CrossRef- Thiol/Disulphide homeostasis, ischemia modified albumin, and ferroxidase as oxidative stress markers in women with obesity with insulin resistance
Elif Ates, Turan Set, Süleyman Caner Karahan, Cemile Biçer, Özcan Erel
Journal of Medical Biochemistry.2019; 38(4): 445. CrossRef - Insulin resistance and chronic kidney disease progression, cardiovascular events, and death: findings from the chronic renal insufficiency cohort study
Sarah J. Schrauben, Christopher Jepson, Jesse Y. Hsu, F. Perry Wilson, Xiaoming Zhang, James P. Lash, Bruce M. Robinson, Raymond R. Townsend, Jing Chen, Leon Fogelfeld, Patricia Kao, J. Richard Landis, Daniel J. Rader, L. Lee Hamm, Amanda H. Anderson, Har
BMC Nephrology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Insulin Based Insulin Resistance with Liver Biomarkers in Type 2 Diabetes mellitus
Usha Adiga, Kathyayani P, Nandith P.B
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2019; 13(2): 1199. CrossRef - Establishment of an ex Vivo Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Using a Tissue-Engineered Liver
Qiao Wu, Juan Liu, Lijin Liu, Yu Chen, Jie Wang, Ling Leng, Qunfang Yu, Zhongping Duan, Yunfang Wang
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2018; 4(8): 3016. CrossRef - Utility of Serum Albumin for Predicting Incident Metabolic Syndrome according to Hyperuricemia
You-Bin Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Seung-Eun Lee, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hwan Jee, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(6): 529. CrossRef - Association of angiotensin-II levels with albuminuria in subjects with normal glucose metabolism, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Se Hee Min, Sung Hye Kong, Jie-Eun Lee, Dong-Hwa Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Kyoung Min Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(10): 1499. CrossRef - Three-dimensional perfused human in vitro model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Tomasz Kostrzewski, Terri Cornforth, Sophie A Snow, Larissa Ouro-Gnao, Cliff Rowe, Emma M Large, David J Hughes
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2017; 23(2): 204. CrossRef - Higher serum albumin was related with diabetes incidence and the impact of BMI changes: Based on cohort study of 18,384 Chinese male elderly
Miao Liu, Jingping Tang, Jing Zeng, Yao He
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(12): 1663. CrossRef - HbA1c as a Screening tool for Ketosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bing Zhu, Le Bu, Manna Zhang, Aaron M. Gusdon, Liang Zheng, Sharvan Rampersad, Jue Li, Shen Qu
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Serum Albumin Concentration and Ketosis Risk in Hospitalized Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Po-Chung Cheng, Shang-Ren Hsu, Yun-Chung Cheng
Journal of Diabetes Research.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Serum Albumin Levels: A Simple Answer to a Complex Problem? Are We on the Right Track of Assessing Metabolic Syndrome?
Sohee Kim, Shinae Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(1): 17. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Detected by Computed Tomography in the General Population Compared with Ultrasonography

- Sustained Maintenance of Normal Insulin-like Growth Factor-I during Pregnancy and Successful Delivery in an Acromegalic Patient with Octreotide-LAR(R) Treatment.
- Soo Kyoung Kim, Jung Hwa Jung, Jae Hyeon Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Alice Hyun Tan, Hee Kyung Kim, Ji In Lee, Hye Soo Chung, Kwang Won Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(3):213-216. Published online September 1, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.3.213
- 1,900 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a 34-year-old Korean woman with active acromegaly and who received Octreotide-LAR(R) for 12 months following transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. During Octreotide-LAR(R) treatment, the clinical improvement was paralleled with the decrease of the growth hormone levels to 1.1 ng/mL and the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) levels to 345.5 ng/mL. Octreotide-LAR(R) was discontinued when the patient was found to be at the 12th week of pregnancy. During pregnancy, the patient experienced clinical well-being and she maintained her IGF-I levels within the normal range for her age-matched despite discontinuation of Octreotide-LAR(R) treatment at early gestation. She delivered a full-term healthy male infant. The serum IGF-I levels of the patient increased progressively increased after delivery. This report describes a successful pregnancy in an acromegalic woman who was exposed to Octreotide-LAR(R) during the early gestational period. She and who showed an unexpected pattern of persistently normal IGF-I levels through the pregnancy despite discontinuation of Octreotide-LAR(R) therapy.

- Clinicopathological Characteristics and Prognostic Factors of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma.
- Hye Won Jang, Ji In Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(3):183-191. Published online September 1, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.3.183
- 2,124 View
- 25 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Studies on the clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic factors of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in Korea are very rare. METHODS: We enrolled 56 MTC patients who underwent surgery at Samsung Medical Center from 1995 to 2006. We analyzed their gender, age at diagnosis, the pathologic findings, the TNM stage, the association with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN), RET protooncogene mutation and the, serum basal calcitonin levels before and after the surgery. We investigated the overall survival and the prognostic factors. RESULTS: The mean age at diagnosis was 46 years and the male/female ratio was 1:2.7. Fine needle aspiration cytology detected 61% of the MTC. The mean tumor size was 2.6 cm (range: 0.2-9.0 cm). Fifty-two percent of patients had the TNM stage more than III at the time of diagnosis. Distant metastasis was found in 5.3% (3/56) of the patients, either at the time of diagnosis or during the follow-up period. Hereditary MTC comprised of 23% of the patients and the disease developed at a younger age (38 years vs. 48 years, respectively, P < 0.05) with more bilaterality. RET protooncogene mutations were found in 27% (9/33) of the patients and most of them were in codon 634. After the primary surgery, the serum basal calcitonin levels were persistently elevated over 13 ng/L in 49% of the patients. The overall 5-year survival rate was 95.5%. Tumor size and distant metastasis were the significant prognostic factors for survival by univariate analysis (P < 0.05). CONCLUSION: There were no significant differences in the clinicopathological characteristics of MTC and survival in Korea compared to those of the Western countries. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preoperative Clinical and Sonographic Predictors for Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastases in Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hye-Seon Oh, Hyemi Kwon, Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Suck Joon Hong, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jung Hwan Baek, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(3): 362. CrossRef - The Relationship between Ultrasonographic Features and Clinical Characteristics of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Min Joon Park, Young Sik Choi, Hee Sung Song, Beom Su Kim
Clinical Ultrasound.2018; 3(1): 8. CrossRef - Dynamic risk stratification for medullary thyroid cancer according to the response to initial therapy
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Ki-Wook Chung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
Endocrine.2016; 53(1): 174. CrossRef - Postoperative biochemical remission of serum calcitonin is the best predictive factor for recurrence‐free survival of medullary thyroid cancer: a large‐scale retrospective analysis over 30 years
Kyong Yeun Jung, Seok‐Mo Kim, Won Sang Yoo, Bup‐Woo Kim, Yong Sang Lee, Kyung Won Kim, Kyu Eun Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Kee‐Hyun Nam, Se Hoon Lee, Jeong Hun Hah, Woong Youn Chung, Ka Hee Yi, Do Joon Park, Yeo‐Kyu Youn, Myung‐Whun Sung, Bo Youn Cho, Cheong Soo
Clinical Endocrinology.2016; 84(4): 587. CrossRef - Changing trends in the clinicopathological features and clinical outcomes of medullary thyroid carcinoma
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Tae‐Yon Sung, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Yu‐Mi Lee, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki‐Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2016; 113(2): 152. CrossRef - Localization of medullary thyroid carcinoma after surgery using 11C-methionine PET/CT: comparison with 18F-FDG PET/CT
Hye Won Jang, Joon Young Choi, Ji In Lee, Hee Kyung Kim, Hyun Won Shin, Jung Hee Shin, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrine Journal.2010; 57(12): 1045. CrossRef
- Preoperative Clinical and Sonographic Predictors for Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastases in Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma

- Retraction: Contributing Factors to Different Natural Courses of Posttansplantation Diabetes Mellitus in Renal Allograft Recipients.
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Myoung Soo Kim, Jae Hyun Nam, Eun Seok Kang, Hyun Joo Lee, So Hun Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Chul Woo Ahn, Soon Il Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(6):479. Published online December 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.6.479
- 1,520 View
- 21 Download

- Contributing Factors to Different Natural Courses of Posttansplantation Diabetes Mellitus in Renal Allograft Recipients.
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Myoung Soo Kim, Jae Hyun Nam, Eun Seok Kang, Hyun Joo Lee, So Hun Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Chul Woo Ahn, Soon Il Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(5):373-381. Published online October 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.5.373
- 1,994 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
New onset diabetes is a major complication after kidney transplantation. However, the natural course of posttransplantation diabetes mellitus (PTDM) remains unclear. The aim of this study was to demonstrate the detailed natural courses of PTDM according to the onset and persistency of hyperglycemia, and to investigate risk factors for development of different courses of PTDM in renal allograft recipients. METHODS: A total of 77 renal allograft recipients without previously known diabetes were enrolled and performed a serial 75 g oral glucose tolerance test at 0, 1, and 7 years after kidney transplantation. Patients were classified according to the onset and persistency of PTDM: early PTMD (E-PTDM), late PTDM (L-PTDM), persistent PTDM (P-PTDM), transient PTMD (T-PTDM), and non-PTDN (N-PTDM). RESULTS: The incidence of each group was as follows: E-PTDM, 39%; L-PTDM, 11.7%; P-PTDM, 23.4% T-PTDM, 15.6%; N-PTDM, 49.3%. Tacrolimus and female gender were associated with the development of E-PTDM. Among E-PTDM, age at transplantation was a high risk factor for the development of P-PTDM. Higher BMI at year1 was associated with the development of L-PTDM. CONCLUSION: Different risk factors were associated with various natural courses of PTDM. Since old age and female gender are not modifiable risk factors, it may be important to modify immunosuppressive therapy regimens for the prevention of E-PTDM and control of body weight for L-PTDM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of Gemigliptin in Post-Transplant Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jaehyun Bae, Youjin Kim, Yongin Cho, Minyoung Lee, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Dong Jin Joo, Kyu Ha Huh, Myoung Soo Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Eun Seok Kang
Transplantation Proceedings.2019; 51(10): 3444. CrossRef - Post-transplantation Diabetes Mellitus
Kun-Ho Yoon
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2006; 21(5): 370. CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of Gemigliptin in Post-Transplant Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

- Adiponectin Gene Polymorphism and Carotid Artery Intima-Media thickness in Type 2 Diabetes.
- Eun Seok Kang, So Young Park, So Hun Kim, Hyun Joo Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Jin Han, Se Eun Park, Hyeong Jin Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(1):29-39. Published online February 1, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.1.29
- 1,778 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to examine the association between the common polymorphisms of the adiponectin gene(ACDC) and the intima-media thickness(IMT) of the common carotid arteries in type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: The B mode ultrasound examination of carotid artery was performed on 133 type 2 diabetic patients. The carotid IMT was calculated using the Intimascope computer program. The SNP45 and SNP276 of the ACDC were examined. RESULTS: There was no significant difference in the carotid IMT among the SNP45 genotypes(0.66+/-0.18mm for TT, 0.71+/-0.12mm for TG and 0.64+/-0.15mm for GG, P=NS). Subjects carrying the SNP276 GG genotype had a markedly lower serum adiponectin concentration than those carrying the TT genotype(3.35+/-2.00microgram/mL vs. 4.98+/-2.24microgram/mL, P=0.029) The carotid IMT was significantly higher in patients with the SNP276 GG genotype than those with the TT genotype (0.70+/-0.17mm vs. 0.59+/-0.13mm, P=0.032). Patients with the +45GG/+276GG genotype combination showed significantly higher mean carotid IMT than the other genotype combinations(0.78+/-0.09mm vs. 0.71+/-0.15mm, P=0.013) CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that the adiponectin gene, SNP276 is associated with the carotid IMT in type 2 diabetic patients. Further studies are will be needed to confirm these genotypephenotype associations.

- A Case of Hypercalcemia Associated with Hepatic Tuberculosis.
- So Young Park, Eun Seok Kang, So Hun Kim, Mi Young Do, Kyu Yeon Hur, Bong Soo Cha, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Sang Hoon Ahn, Young Myoung Moon, Young Nyun Park
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(1):64-68. Published online February 1, 2004
- 1,222 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this report, a 70-year-old female patient was detected with laboratory findings of hypercalcemia. The most common causes of hypercalcemia are primary hyperparathyroidism and malignant disease. Her laboratory tests did not show any evidence for neither primary hyperparathyroidism nor malignant diseases. Thus, granulomatous disease was suspected as the cause of the hypercalcemia. Liver MRI (magnetic resonance image) was performed on the subject, which suggested the presence of hepatic tuberculosis and sarcoidosis. Because the chest x-ray did not show a definite tuberculous lesion, we performed a laparoscopic liver biopsy for a final diagnosis. Findings from the biopsy specimen showed typical tuberculosis. After treatment with tuberculosis medication, hypercalcemia of the subject was resolved. Hypercalcemia is a well recognized as a possible complication of active pulmonary tuberculosis. But one should consider hepatic tuberculosis without pulmonary tuberculosis as a cause of hypercalcemia.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



